
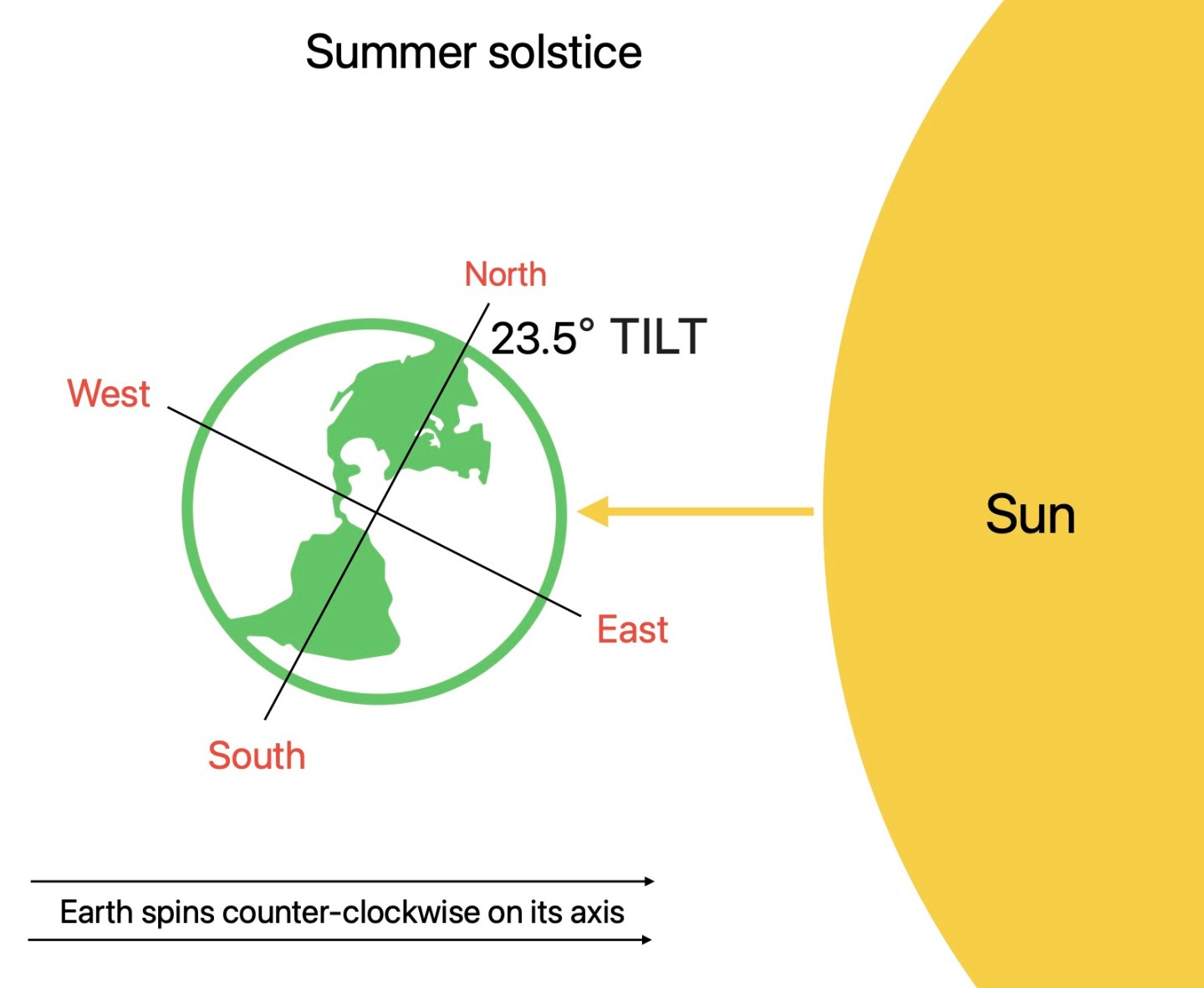
The earth is tilted on its axis by approximately 23.5° (Degrees). This means the sun appears shifted sometimes. It rises directly in the east and sets directly in the west only twice a year. The tilt is also the cause of the different seasons.
For the Northern hemisphere in March, the sun appears directly east. This is known as the vernal equinox. Then the sun shifts northeast until June (this is called the summer solstice). The sun then shifts back until it appears directly east again which is known as the autumn equinox in September. After, the sun appears to shift toward the southeast. This occurs until the winter solstice in December. Then the sun shifts back until it’s directly east again which is the vernal equinox in March. The cycle repeats.
Definitions
Vernal means spring.
Equinox is when the sun appears directly over the equator positioned at an equal distance to the north as it is to the south. The days and nights are supposed to be an equal duration.
The vernal equinox marks the beginning of the spring season in the northern hemisphere.
Summer Solstice marks the beginning of the summer season in the northern hemisphere. It is the longest day of the year and the shortest night. The sun is closer to the northern hemisphere hence why it is hotter.
Winter solstice marks the beginning of the winter season in the northern hemisphere. It is the shortest day of the year and the longest night. The sun is furthest away from the northern hemisphere hence why it is colder.